Using xrt as x-ray calculator¶
xrt can be used as a library for calculations of synchrotron sources and material properties related to x-ray scattering, diffraction and propagation: reflectivity, transmittivity, refractive index, absorption coefficient etc.
See the scripts in \examples\withRaycing\00_xRayCalculator\.
Each script consists of:
imports, with possibly defining a path to xrt if it is installed in a non-standard location,
a definition of a source or a material object,
invocation of a corresponding method of interest for a specified range of energy, angles etc. and
plotting.
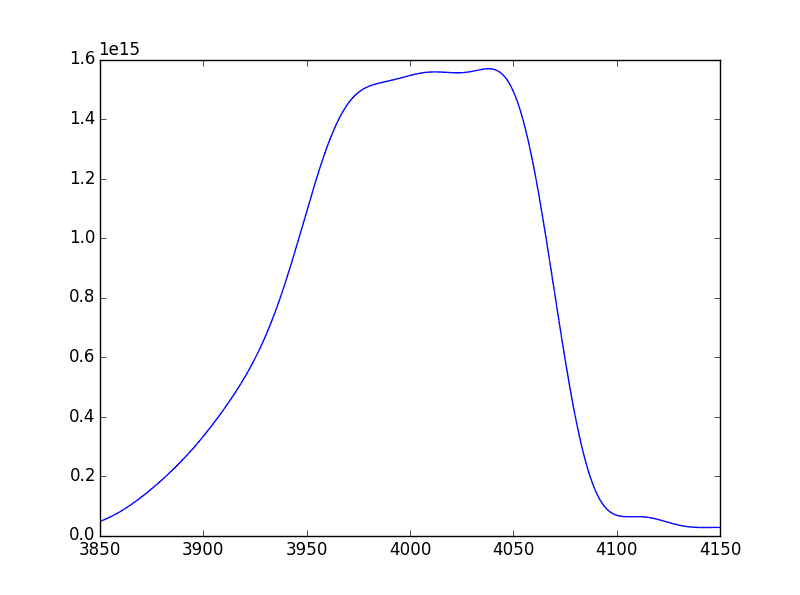
Example 1a: Undulator
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys; sys.path.append(r"c:\Ray-tracing")
import xrt.backends.raycing.sources as rs
source = rs.Undulator(eE=3.0, eI=0.5, eEpsilonX=0.263, eEpsilonZ=0.008,
betaX=9.539, betaZ=1.982, period=18.5, n=108, K=0.52, distE='BW')
energy = np.linspace(3850, 4150, 601)
theta = np.linspace(-1, 1, 51) * 30e-6
psi = np.linspace(-1, 1, 51) * 30e-6
I0, l1, l2, l3 = source.intensities_on_mesh(energy, theta, psi)
dtheta, dpsi = theta[1] - theta[0], psi[1] - psi[0]
flux = I0.sum(axis=(1, 2)) * dtheta * dpsi
plt.plot(energy, flux)
plt.show()
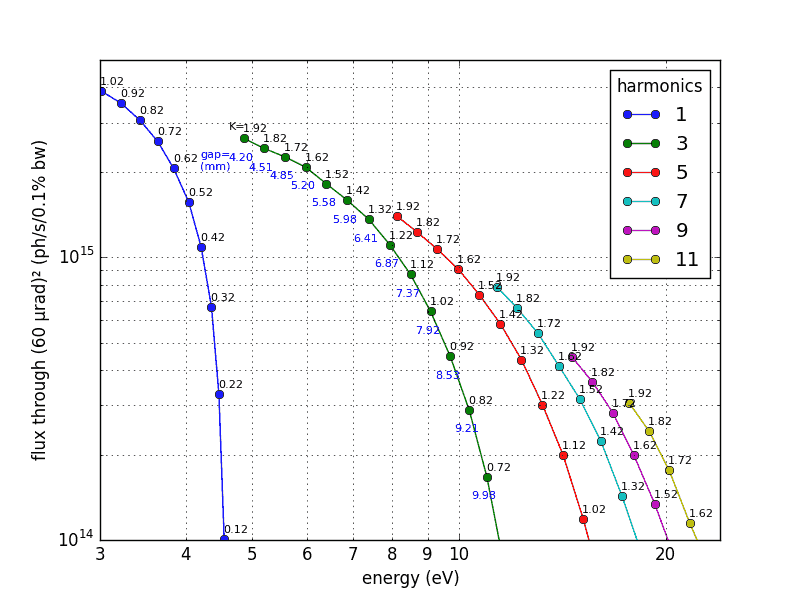
Example 1b: Undulator, tuning curves
Use the method:
tunesE, tunesF = source.tuning_curves(energy, theta, psi, harmonics, Ks)
See the script
\examples\withRaycing\00_xRayCalculator\calc_undulator_tune.py.
Example 2a: Crystal reflectivity
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys; sys.path.append(r"c:\Ray-tracing")
import xrt.backends.raycing.materials as rm
crystal = rm.CrystalSi(hkl=(1, 1, 1))
E = 9000
dtheta = np.linspace(-20, 80, 501)
theta = crystal.get_Bragg_angle(E) + dtheta*1e-6
curS, curP = crystal.get_amplitude(E, np.sin(theta))
plt.plot(dtheta, abs(curS)**2, 'r', dtheta, abs(curP)**2, 'b')
plt.show()
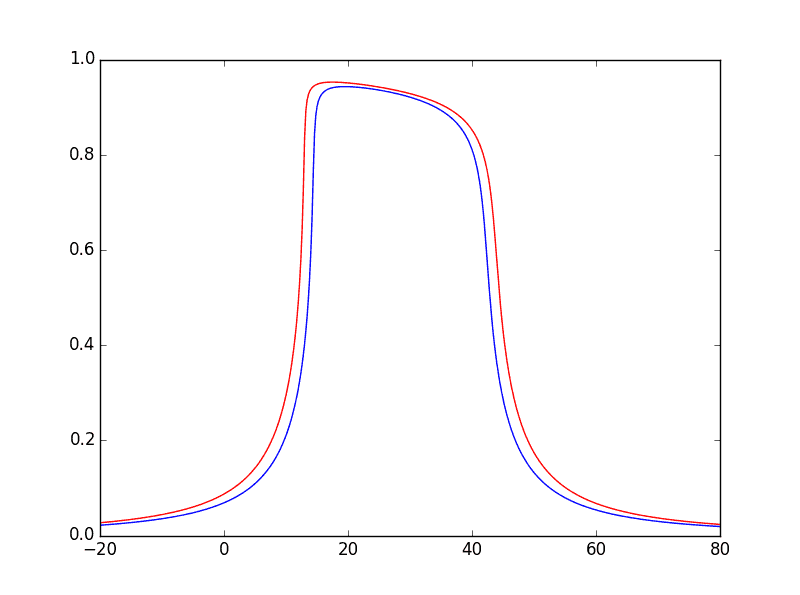
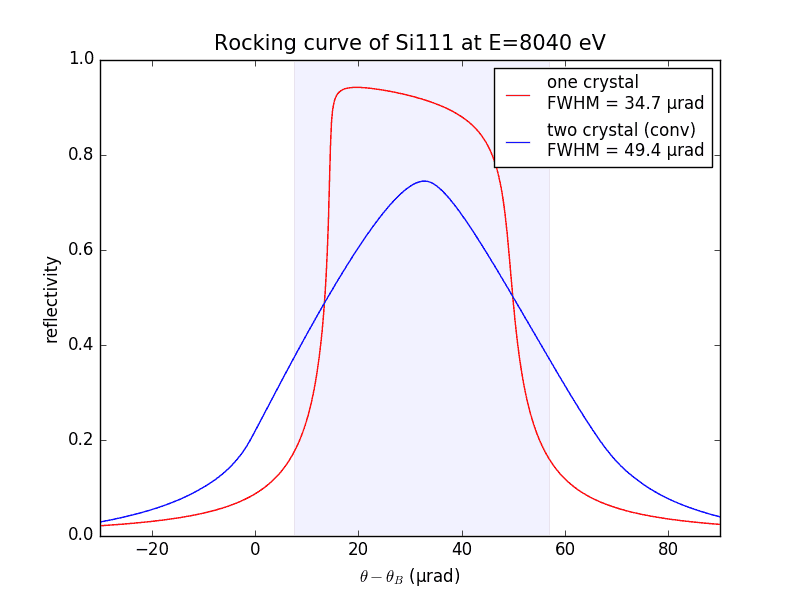
Example 2b: Crystal reflectivity: Single and double crystal
See the script
\examples\withRaycing\00_xRayCalculator\calc_crystal_rocking_curve.py.
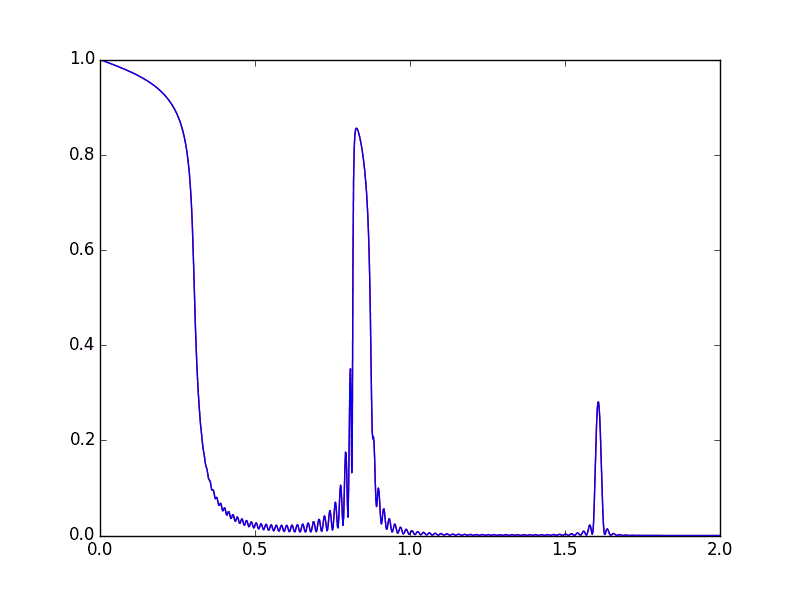
Example 3: Multilayer reflectivity
mSi = rm.Material('Si', rho=2.33)
mW = rm.Material('W', rho=19.3)
mL = rm.Multilayer(mSi, 27, mW, 18, 40, mSi)
E = 10000
theta = np.linspace(0, 2.0, 1001) # degrees
rs, rp = mL.get_amplitude(E, np.sin(np.deg2rad(theta)))[0:2]
plt.plot(theta, abs(rs)**2, 'r', theta, abs(rp)**2, 'b')
plt.show()
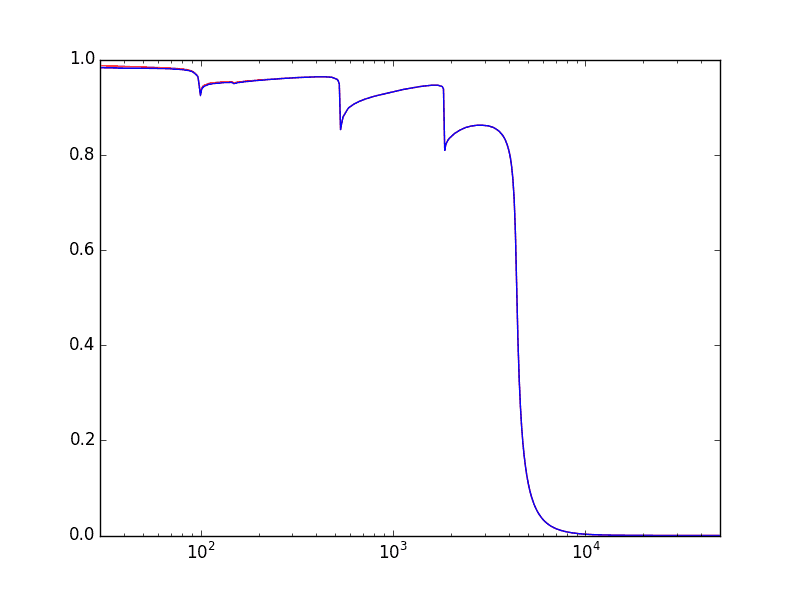
Example 4: Mirror reflectivity
stripe = rm.Material(('Si', 'O'), quantities=(1, 2), rho=2.2)
E = np.logspace(1 + np.log10(3), 4 + np.log10(5), 501)
theta = 7e-3
rs, rp = stripe.get_amplitude(E, np.sin(theta))[0:2]
plt.semilogx(E, abs(rs)**2, 'r', E, abs(rp)**2, 'b')
plt.gca().set_xlim(E[0], E[-1])
plt.show()
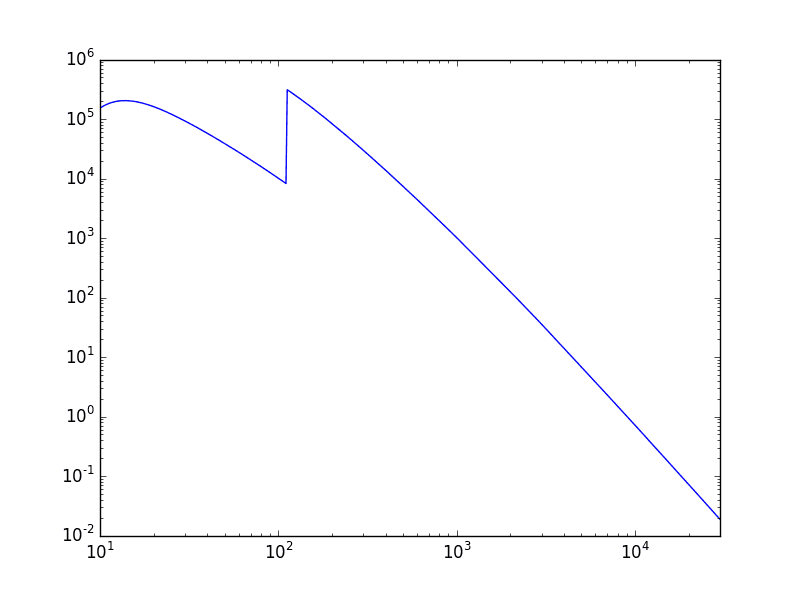
Example 5: Material absorption
mat = rm.Material('Be', rho=1.848)
E = np.logspace(1, 4 + np.log10(3), 501)
mu = mat.get_absorption_coefficient(E)
plt.loglog(E, mu)
plt.gca().set_xlim(E[0], E[-1])
plt.show()